Hydrochloric acid (HCl) is a fundamental chemical with a wide range of industrial applications, including chemical manufacturing, metal processing, and food production. It is a colorless and highly corrosive liquid, and it is primarily produced through two main processes: the chlorination of organic compounds and the reaction of sulfuric acid with sodium chloride. This blog will provide an in-depth look at the production process of hydrochloric acid, covering various aspects such as manufacturing techniques, raw material costs, market prices, and the latest industry news.
Manufacturing Report and Process
Hydrochloric acid production involves several methods, but the most common are the direct synthesis method and the by-product method.
Direct Synthesis Method
The direct synthesis method, also known as the direct combination method, involves the chemical reaction between hydrogen gas (H2) and chlorine gas (Cl2).
Request For Sample: https://www.procurementresource.com/production-cost-report-store/hydrochloric-acid/request-sample
In this process, hydrogen and chlorine gases are fed into a reactor where they react to form hydrochloric acid. The reaction is controlled to prevent the formation of unwanted by-products, and the resulting hydrochloric acid gas is then absorbed in water to produce the liquid form of HCl.
By-Product Method
The by-product method involves the production of hydrochloric acid as a secondary product during the manufacture of other chemicals. One common example is the production of HCl during the chlorination of organic compounds such as methane to produce chloromethanes.
In this method, hydrochloric acid is produced as a by-product and is captured and purified for commercial use.
Manufacturing Steps
- Feed Preparation: Raw materials, including hydrogen and chlorine gases, are prepared and purified.
- Reaction: The gases are reacted in a controlled environment to produce HCl gas.
- Absorption: The HCl gas is absorbed in water to form aqueous hydrochloric acid.
- Purification: The acid is purified to remove any impurities and achieve the desired concentration.
- Packaging and Storage: The final product is packaged and stored for distribution.
Raw Material Costs
The cost of raw materials plays a significant role in the overall production cost of hydrochloric acid. The primary raw materials used in the production process are hydrogen gas and chlorine gas.
Hydrogen Gas
Hydrogen gas can be produced through various methods, including natural gas reforming, electrolysis of water, and by-product recovery from industrial processes. The cost of hydrogen gas varies depending on the production method and the prevailing market conditions. Factors such as natural gas prices, electricity costs, and technological advancements in hydrogen production can influence the cost.
Chlorine Gas
Chlorine gas is primarily produced through the electrolysis of sodium chloride (common salt). The cost of chlorine gas is influenced by the price of electricity, the efficiency of the electrolysis process, and the availability of raw materials. Market demand for chlorine and its by-products also affects the price.
Overall Cost Analysis
The combined cost of hydrogen and chlorine gases, along with other operational expenses such as labor, energy, and maintenance, determines the total cost of producing hydrochloric acid. Fluctuations in the prices of these raw materials directly impact the production cost and, consequently, the market price of hydrochloric acid.
Hydrochloric Acid Market Price
Hydrochloric acid is traded globally, and its market price is influenced by several factors, including production costs, demand and supply dynamics, and regional market conditions.
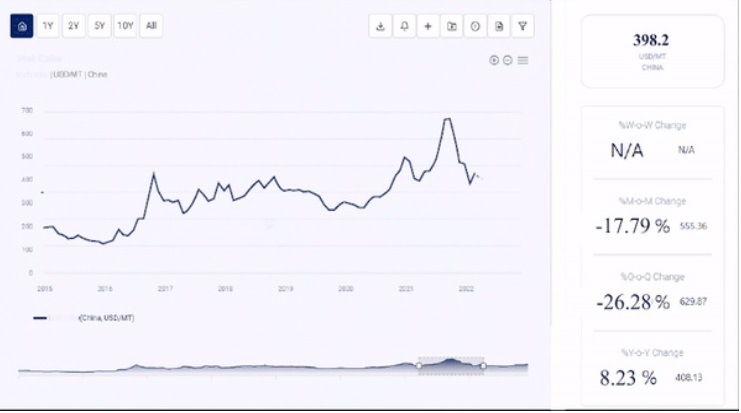
Hydrochloric Acid Price per Ton
As of the latest data, the price of hydrochloric acid varies depending on its concentration and purity. Industrial-grade hydrochloric acid (30-35% concentration) is typically priced between $200 to $300 per ton. However, prices can fluctuate based on market conditions, availability of raw materials, and regional demand. For instance, prices might be higher in regions with limited production capacity or during periods of high demand.
Market Dynamics
The demand for hydrochloric acid is driven by its extensive use in various industries such as:
- Chemical Manufacturing: Used as a reagent in the production of various chemicals.
- Metal Processing: Essential for pickling and cleaning metals.
- Food Industry: Utilized in food processing and as an additive.
- Water Treatment: Employed for pH control and neutralization.
Supply disruptions, changes in production capacities, and economic conditions also play a crucial role in determining the market price of hydrochloric acid.
Latest News
The hydrochloric acid market is continually evolving, with new developments and trends shaping the industry. Some of the latest news and trends include:
Environmental Regulations
Stricter environmental regulations are influencing the production and usage of hydrochloric acid. Manufacturers are investing in cleaner and more efficient production technologies to comply with environmental standards and reduce emissions.
Technological Advancements
Advancements in production technologies, such as more efficient electrolysis processes and improved absorption techniques, are enhancing the efficiency and sustainability of hydrochloric acid production.
Market Expansion
The global hydrochloric acid market is witnessing expansion, particularly in emerging economies where industrialization and urbanization are driving demand. Countries in Asia-Pacific, Latin America, and Africa are experiencing increased consumption of hydrochloric acid.
Strategic Partnerships
Companies are forming strategic partnerships and collaborations to enhance their production capabilities and expand their market reach. These partnerships are aimed at leveraging synergies and achieving cost efficiencies.
Supply Chain Challenges
The hydrochloric acid market is facing supply chain challenges due to disruptions caused by geopolitical tensions, natural disasters, and global pandemics. These challenges are impacting the availability and cost of raw materials, as well as the distribution of the final product.
Conclusion
Hydrochloric acid is a vital chemical with diverse industrial applications. Understanding the production process, raw material costs, and market dynamics is essential for stakeholders in the industry. The market price of hydrochloric acid is influenced by a range of factors, including production costs, demand-supply balance, and regional conditions. Staying informed about the latest news and trends can help businesses navigate the complexities of the hydrochloric acid market and make informed decisions.