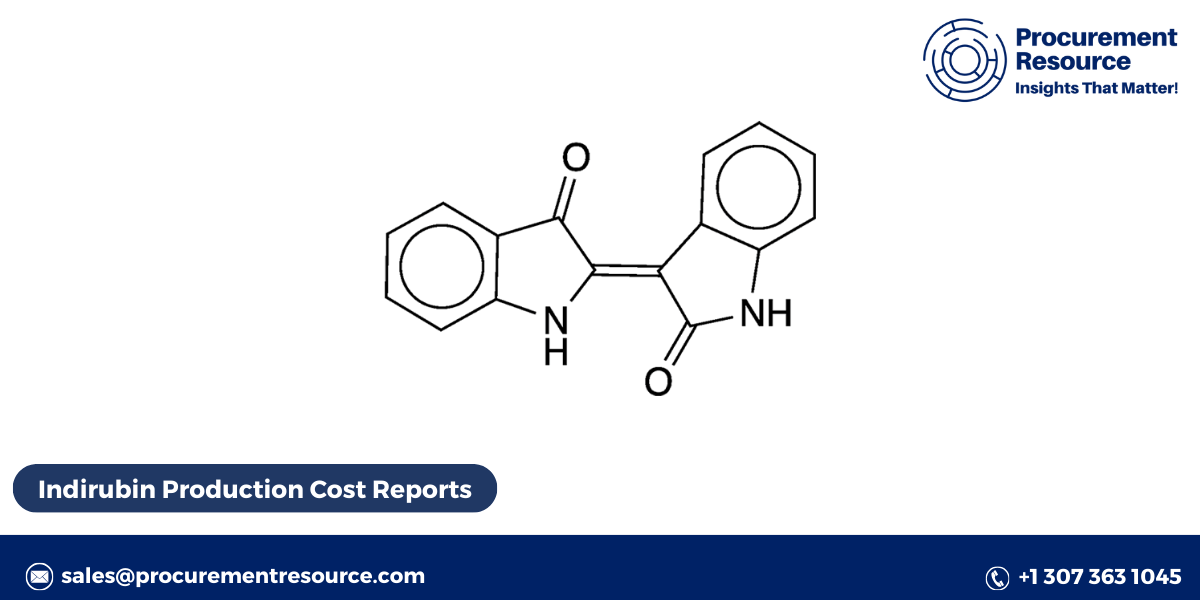
Indirubin, a naturally occurring indole compound, is recognized for its pharmacological properties, particularly its use in traditional Chinese medicine and as a promising agent in the treatment of leukemia, inflammatory diseases, and certain cancers. It is an isomer of indigo and is a key component of the herbal medicine Danggui Longhui Wan. The increasing interest in indirubin’s potential therapeutic uses has driven demand for efficient and scalable production methods. This report delves into the key stages and technologies involved in the production of indirubin, the challenges in the process, and future trends in indirubin manufacturing.
Overview of Indirubin
Indirubin (C16H10N2O2) is a reddish-blue pigment with a molecular structure that allows it to inhibit various protein kinases, contributing to its anti-inflammatory, anticancer, and anti-viral properties. The compound is a derivative of indigo and belongs to the class of bisindole alkaloids. While indirubin can be extracted from natural sources such as indigo plants (Indigofera tinctoria), advanced biotechnological methods are increasingly being employed to optimize its production, especially for pharmaceutical applications.
Request For Sample: https://www.procurementresource.com/production-cost-report-store/indirubin/request-sample
Natural Extraction of Indirubin
Indirubin is traditionally extracted from plants like Indigofera tinctoria and Isatis tinctoria, which also produce indigo. The natural extraction process involves the following steps:
a. Harvesting of Plant Material: Plants are harvested at the appropriate growth stage to maximize indirubin content. Optimal conditions for indirubin synthesis are important, including exposure to sunlight and specific soil pH levels.
b. Solvent Extraction: The plant material is dried, ground, and subjected to solvent extraction using solvents such as ethanol or methanol. The solvents dissolve the indirubin and other related indole compounds.
c. Filtration and Evaporation: The mixture is filtered to remove solid plant matter, leaving behind the indirubin-laden solution. Solvent evaporation concentrates the indirubin extract, which is then purified through crystallization or chromatography techniques to obtain high-purity indirubin.
d. Purification: Purification methods, including silica gel chromatography, are used to separate indirubin from other compounds such as indigo. Multiple purification cycles may be required to reach the desired purity level, especially for pharmaceutical-grade indirubin.
Synthetic Production of Indirubin
Although natural extraction is effective, the yield is typically low, which limits its scalability. To meet growing demand, researchers have developed synthetic and semi-synthetic methods for indirubin production. The synthetic pathway offers a controlled and scalable alternative for large-scale production.
a. Chemical Synthesis: Indirubin can be chemically synthesized through various methods, often starting with indole and isatin derivatives. One of the common synthesis pathways is the condensation of isatin with indoxyl acetate, leading to the formation of indirubin. The process typically involves:
- Step 1: Preparation of Isatin: Isatin is synthesized from aniline through a series of chemical reactions involving oxidation and ring closure. It serves as a precursor for indirubin.
- Step 2: Condensation Reaction: Isatin reacts with indoxyl acetate or another suitable indole derivative under specific temperature and pH conditions to yield indirubin.
- Step 3: Purification: The crude indirubin is purified using recrystallization, column chromatography, or high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC), depending on the required purity level.
b. Enzymatic Synthesis: Advances in biotechnology have introduced enzymatic methods to produce indirubin. These methods leverage enzymes like peroxidases, which catalyze the coupling of indole compounds under mild conditions, making the process more environmentally friendly and potentially more cost-effective. Enzymatic synthesis often employs genetically engineered microorganisms such as Escherichia coli to produce indirubin precursors, which are then converted into indirubin by enzymatic activity.
Biotechnological Approaches
Recent advances in metabolic engineering have made it possible to produce indirubin through microbial fermentation. This process involves genetically modifying microorganisms to enhance the production of indirubin precursors such as indoxyl. These biotechnological methods offer several advantages, including the ability to use renewable feedstocks, reduce environmental impact, and scale production efficiently.
a. Genetic Engineering of Microbes: Scientists modify the metabolic pathways of bacteria like E. coli or yeast to overproduce indirubin precursors. By introducing genes that encode key enzymes in the indirubin biosynthesis pathway, these microbes can be cultured in bioreactors to produce indirubin at high yields.
b. Fermentation Process: The fermentation process involves cultivating genetically engineered microbes in a nutrient-rich medium under controlled conditions (temperature, pH, oxygen levels) to maximize indirubin production. Post-fermentation, indirubin is extracted, purified, and processed for pharmaceutical or industrial use.
c. Optimization of Production Conditions: Continuous research focuses on optimizing fermentation parameters, such as feedstock composition and bioreactor conditions, to improve indirubin yield and reduce production costs. Scaling up from laboratory conditions to industrial-scale bioreactors is a key challenge in this approach.
Challenges in Indirubin Production
Despite the promising developments in indirubin production, several challenges remain:
a. Low Yield in Natural Extraction: Natural sources of indirubin produce the compound in low quantities, requiring large amounts of plant material for even small yields. This not only makes the process inefficient but also puts pressure on the natural resources.
b. Purity and Consistency: Achieving consistent purity is critical for indirubin used in pharmaceuticals. The presence of impurities can affect the efficacy and safety of the final product. Both natural extraction and synthetic methods need to implement rigorous purification techniques.
c. Cost-Effectiveness: While synthetic methods allow for large-scale production, the cost of raw materials and complex purification processes can drive up the production costs. Biotechnological approaches, while cost-effective in the long run, require significant initial investments in research and development.
d. Environmental Considerations: Chemical synthesis often involves toxic reagents and solvents, which pose environmental risks. Green chemistry and biotechnological methods are being explored to reduce the environmental impact of indirubin production.
Future Trends in Indirubin Production
As research continues to reveal the potential therapeutic applications of indirubin, several trends are expected to shape its production in the coming years:
a. Bioprocessing Technologies: The use of genetically engineered microorganisms for indirubin production is likely to gain momentum. Advances in metabolic engineering, CRISPR technologies, and bioreactor design will contribute to more efficient and sustainable production processes.
b. Green Chemistry: Efforts to reduce the environmental impact of indirubin production will drive the development of green chemistry approaches. These methods will focus on reducing the use of harmful reagents and solvents while improving yield and purity.
c. Pharmaceutical Applications: The growing demand for indirubin in cancer research and its role as an anti-inflammatory agent will likely push for more investment in the development of novel indirubin-based drugs. This, in turn, will necessitate the scaling up of production technologies.
Indirubin production, whether through natural extraction, chemical synthesis, or biotechnological methods, presents both opportunities and challenges. The continuous evolution of production techniques aims to meet the increasing demand for high-purity indirubin, especially in the pharmaceutical sector. Biotechnological advances hold the promise of more sustainable and cost-effective production methods, shaping the future of indirubin manufacturing.
Contact Us:
Company Name: Procurement Resource
Contact Person: Endru Smith
Email: sales@procurementresource.com
Toll-Free Number: USA & Canada - Phone no: +1 307 363 1045 | UK - Phone no: +44 7537 132103 | Asia-Pacific (APAC) - Phone no: +91 1203185500
Address: 30 North Gould Street, Sheridan, WY 82801, USA
Website: https://www.procurementresource.com/