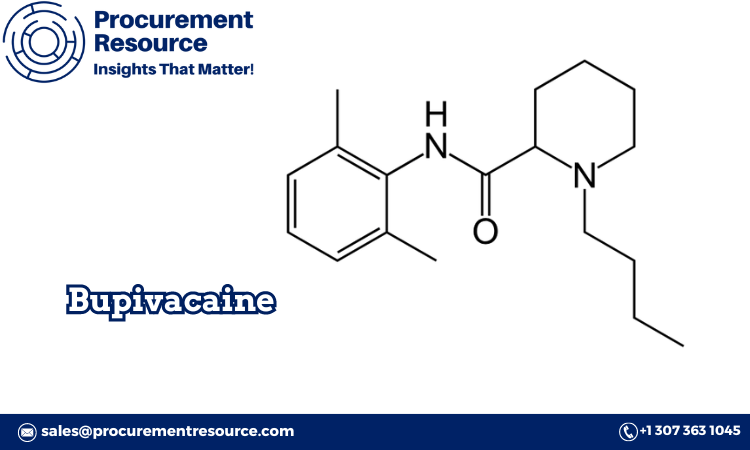
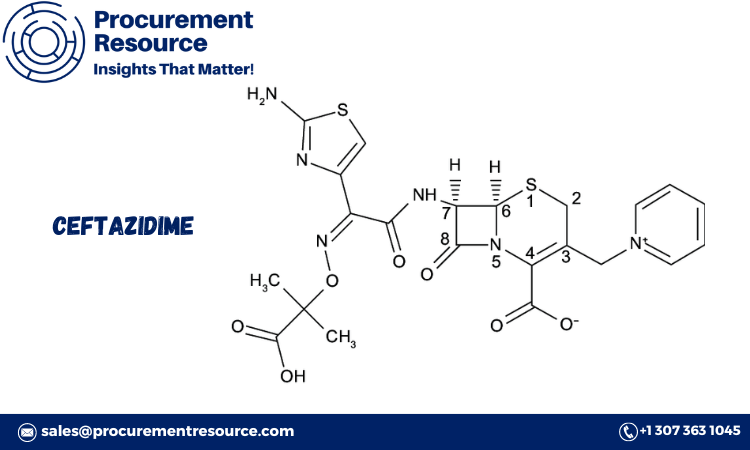
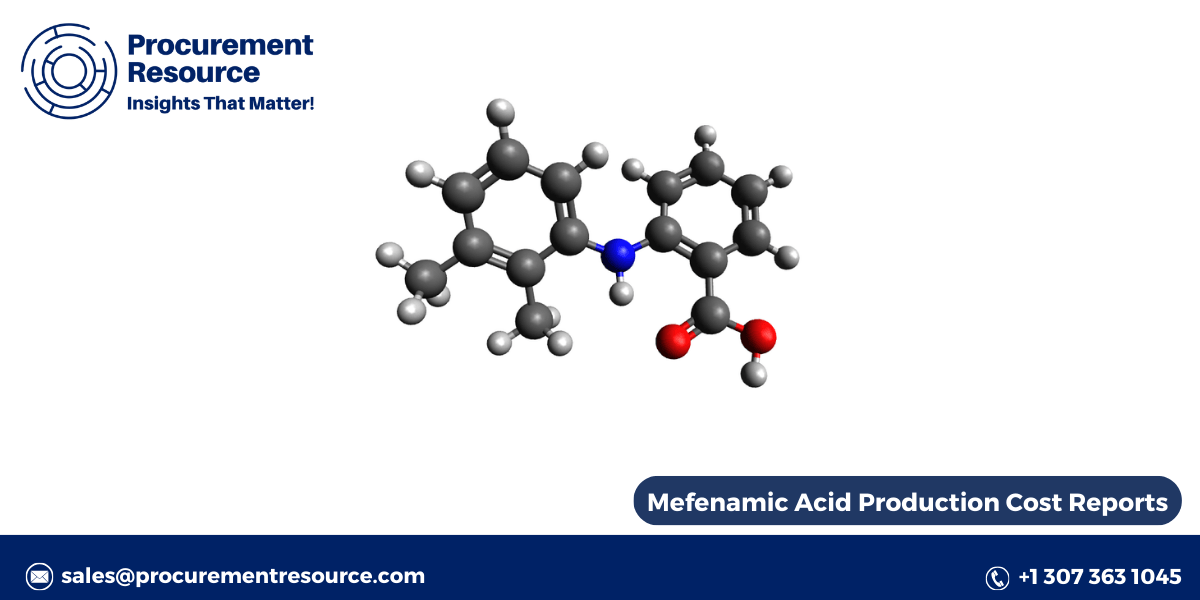
Carbon nanotubes (CNTs) are unique cylindrical carbon structures renowned for their extraordinary electrical, thermal, and mechanical properties. These properties have paved the way for their use in a wide range of applications, from electronics and nanotechnology to energy storage and medical devices. This report explores the carbon nanotubes production process, key factors that influence the cost of production, and trends in carbon nanotube prices.
Carbon Nanotubes Production Process
The production of carbon nanotubes primarily involves three common techniques:
- Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD): CVD is the most widely used method for synthesizing carbon nanotubes. In this process, a hydrocarbon gas (such as methane or acetylene) is introduced into a high-temperature reactor, where it decomposes to form carbon atoms. These atoms then assemble into nanotubes on a catalyst substrate. The CVD process allows for the precise control of nanotube structure, length, and diameter, making it suitable for large-scale production.
- Arc Discharge: The arc discharge method involves passing a high electrical current through graphite electrodes in an inert gas atmosphere. This current generates a high-temperature arc, vaporizing carbon from the electrodes and forming nanotubes in the process. While this method can produce high-quality carbon nanotubes, it is often less efficient and cost-effective for mass production.
- Laser Ablation: Laser ablation uses high-power laser pulses to vaporize graphite in a high-temperature reactor. The vaporized carbon atoms condense on a cooler surface, forming nanotubes. This method yields high-purity nanotubes, though it is more expensive than CVD and generally limited to research or small-scale applications.
Request For Sample: https://www.procurementresource.com/production-cost-report-store/carbon-nanotubes/request-sample
Cost of Carbon Nanotubes Production
Several factors contribute to the cost of producing carbon nanotubes, including:
- Raw Materials: The type and cost of raw materials, including carbon sources (methane, acetylene, or graphite) and catalysts (like nickel or cobalt), play a significant role in the overall cost structure.
- Energy Consumption: The high temperatures required in the CVD and arc discharge processes lead to substantial energy costs. Efficient energy management can, therefore, reduce production costs.
- Equipment and Technology: Specialized equipment such as reactors, lasers, or arc chambers are essential for nanotube production. Advanced technologies that improve production efficiency often come with higher upfront costs.
- Labor Costs: Production and quality control processes require skilled labor, which adds to the operational cost. Automation and optimized production methods can help reduce these costs.
- Production Scale: Large-scale production generally reduces the unit cost of carbon nanotubes due to economies of scale. As the demand for carbon nanotubes rises, manufacturers are increasing production capacity, which helps bring down costs over time.
Carbon Nanotubes Price Trends
The price of carbon nanotubes can vary widely depending on factors such as:
- Purity: Higher purity nanotubes are typically more expensive, as they require additional processing and refinement. Single-walled carbon nanotubes (SWCNTs), for example, are generally pricier than multi-walled carbon nanotubes (MWCNTs) due to their enhanced properties and more complex production process.
- Application Requirements: Carbon nanotubes used in electronics, medical devices, and aerospace applications often command higher prices because of the stringent quality and performance standards.
- Market Demand: As industries such as electronics, automotive, and healthcare adopt CNTs, demand has surged. This increase in demand has pushed manufacturers to improve production efficiency, which has, in turn, led to more competitive pricing.
- Technological Advancements: New techniques and production methods continue to emerge, allowing for cost reduction in nanotube production. Methods that optimize material use and reduce waste contribute to lower production costs and subsequently lower market prices.
Future Outlook for Carbon Nanotubes Production and Costs
The carbon nanotube industry is expected to grow as more applications are discovered and existing technologies improve. The push for sustainability has led to research on cost-effective, eco-friendly production methods, which may lower costs further. Additionally, as large-scale production facilities become more prevalent, economies of scale will likely drive prices down, making CNTs more accessible for various industries.
Conclusion
The production of carbon nanotubes is a sophisticated process with a variety of methods, each impacting the final cost. Factors such as raw materials, energy use, and technological advancements are critical in shaping the cost of CNT production. As technology progresses, the production cost of carbon nanotubes is expected to decrease, enabling broader applications and adoption across multiple industries. By staying informed on the latest trends in CNT production and pricing, businesses can make strategic decisions to leverage this promising material in their own applications.
Contact Us:
Company Name: Procurement Resource
Contact Person: Endru Smith
Email: sales@procurementresource.com
Toll-Free Number: USA & Canada - Phone no: +1 307 363 1045 | UK - Phone no: +44 7537 132103 | Asia-Pacific (APAC) - Phone no: +91 1203185500
Address: 30 North Gould Street, Sheridan, WY 82801, USA