Introduction: L-carnitine Production Process with Cost Analysis
The L-carnitine Production Process is essential for multiple industries, including nutraceuticals, pharmaceuticals, and animal feed. As an important compound known for its role in energy metabolism, L-carnitine production involves specific techniques and high-quality resources to meet industry standards. This report provides a comprehensive overview of the production process, covering cost analysis, resource procurement, market drivers, and critical factors impacting production costs, offering valuable insights for stakeholders looking to optimize production or enter this growing market.
Request Free Sample – https://www.procurementresource.com/production-cost-report-store/l-carnitine/request-sample
Procurement Resource Assessment: L-carnitine Production Process
A thorough Procurement Resource Assessment is crucial for optimizing the L-carnitine production process. This assessment involves evaluating the availability, quality, and cost-effectiveness of essential resources, including raw materials, labor, equipment, and energy.
L-carnitine is typically produced through two primary methods:
- Chemical Synthesis: This method involves the use of chemical reactions to produce L-carnitine. Chemical synthesis can be cost-effective on a large scale but requires precise control to ensure the chirality of the final product, as only the L-form of carnitine is biologically active.
- Biotechnological Production: This method leverages biotechnological processes, such as fermentation using specific microbial strains, to produce L-carnitine. This approach is more sustainable and is becoming increasingly popular, particularly for high-quality and natural-sourced products in the nutraceutical and pharmaceutical sectors.
By conducting a comprehensive resource assessment, companies can identify reliable suppliers for high-quality raw materials, implement cost-efficient sourcing strategies, and establish a robust supply chain, all of which are essential for consistent and compliant production.
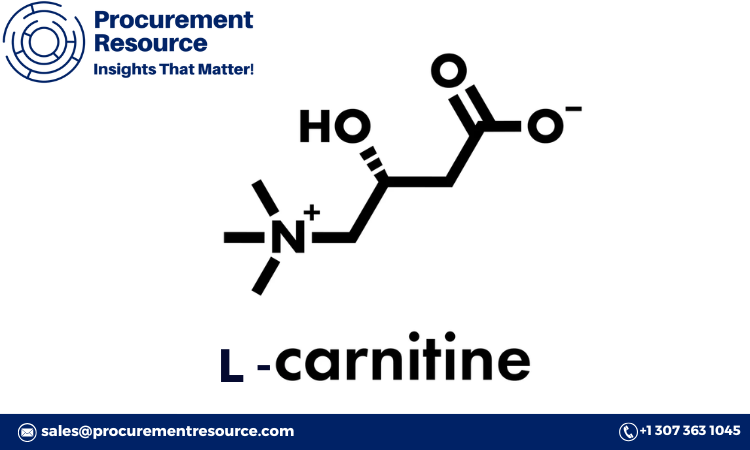
L-carnitine Overview
L-carnitine is a naturally occurring amino acid derivative involved in energy production. It facilitates the transport of fatty acids into the mitochondria, where they are oxidized to produce energy. Due to its role in energy metabolism, L-carnitine is commonly used as a dietary supplement for athletes, those looking to enhance weight loss, and individuals with certain health conditions that affect energy levels, such as chronic fatigue syndrome and heart disease.
In addition to its uses in human health, L-carnitine is used in the animal feed industry to improve energy metabolism and growth in livestock. It is also included in some pet foods and nutritional supplements, particularly for older pets or animals with certain health conditions. The multifaceted benefits of L-carnitine have contributed to its high demand across various sectors, making efficient and cost-effective production crucial to meet market needs.
Market Drivers
Several Market Drivers are influencing the demand for L-carnitine:
- Increased Interest in Health and Wellness: The demand for L-carnitine supplements has grown in line with consumer interest in health and wellness. As more people pursue active lifestyles and prioritize nutrition, products like L-carnitine, which support energy and fat metabolism, have become popular.
- Rising Demand in Sports Nutrition: L-carnitine is commonly used in sports nutrition for its potential to enhance exercise performance and recovery. The expanding sports nutrition market, driven by both amateur and professional athletes, has increased demand for L-carnitine-based products.
- Expanding Applications in Animal Nutrition: L-carnitine is widely used in animal feed to improve metabolism, growth, and overall health in livestock. As the animal nutrition industry grows, demand for ingredients like L-carnitine continues to rise.
- Growing Awareness of Heart Health: L-carnitine’s role in supporting cardiovascular health has led to increased interest in the compound as part of heart health supplements. The aging population, along with a rise in awareness of heart health, has fueled demand for products containing L-carnitine.
- Advancements in Biotechnology and Green Production Methods: Innovations in biotechnological processes have made it easier to produce L-carnitine sustainably. The increasing preference for eco-friendly production methods, particularly in the nutraceutical sector, has contributed to the adoption of biotechnological approaches to L-carnitine production.
Raw Materials Requirements
The Raw Materials Requirements for L-carnitine production depend on the specific production method used. Key raw materials include:
- Starting Chemical Compounds: For chemical synthesis, raw materials such as trimethylamine and crotonic acid are commonly used. The choice of compounds depends on the specific synthetic pathway and desired product purity.
- Microbial Strains and Nutrient Media: In biotechnological production, specific microbial strains, such as bacteria or yeast, are used to convert precursor compounds into L-carnitine. Nutrient media, including carbon sources like glucose and essential minerals, support microbial growth and metabolic activity.
- Solvents: Solvents, such as ethanol or methanol, are used throughout the synthesis and purification stages. Solvents help dissolve reagents, control reaction conditions, and assist in isolating the final product.
- Catalysts and Enzymes: Chemical synthesis may require catalysts to enhance reaction rates and yields. For biotechnological processes, specific enzymes may be used to facilitate the conversion of substrates into L-carnitine.
- Water: Water is essential for various stages of the production process, from reaction media to cooling and cleaning. Effective water management is critical to ensure cost-effectiveness and environmental sustainability.
Costs and Key Process Information
Understanding the Costs and Key Process Information is essential for optimizing the L-carnitine production process. Major cost components include raw materials, labor, equipment, energy, and compliance with regulatory standards.
- Raw Material Costs: The cost of starting compounds, such as trimethylamine, catalysts, and solvents, represents a significant portion of production expenses. Efficient sourcing strategies help mitigate cost volatility in these essential inputs.
- Labor Costs: Skilled labor is required for various stages of production, including chemical synthesis, microbial fermentation, purification, and quality control. Labor costs vary depending on the geographic location and production scale.
- Equipment and Facility Costs: L-carnitine production facilities require specialized equipment, such as reactors, fermenters, and filtration systems, for synthesis and purification. Initial capital investments are substantial, particularly for large-scale production. Ongoing maintenance costs are necessary to ensure safety and operational efficiency.
- Energy Costs: The production process is energy-intensive, especially during chemical synthesis and microbial fermentation. Efficient energy management is critical to minimizing costs and reducing the environmental impact of production. Many producers are exploring renewable energy options to enhance sustainability.
- Environmental Compliance: L-carnitine production is subject to environmental regulations, particularly regarding emissions, waste management, and water usage. Compliance with these regulations involves investments in emissions control systems, wastewater treatment, and documentation, contributing to overall production costs.
Looking for an Exhaustive and Personalized Report that Could Significantly Substantiate Your Business
For stakeholders seeking a comprehensive understanding of the L-carnitine production process, a Personalized Report provides tailored insights specific to your business needs. Such a report offers:
- A detailed breakdown of production costs and potential cost-saving measures.
- Recommendations for sourcing high-quality raw materials and establishing reliable supplier relationships.
- Market analysis, including trends, competitive landscape, and growth opportunities within the nutraceutical and animal nutrition industries.
- Guidance on optimizing energy use, waste management, and environmental sustainability.
- Insights into regulatory compliance and quality control measures to ensure adherence to industry standards and maintain product integrity.
An exhaustive, data-driven report provides the critical information necessary to navigate the complexities of the L-carnitine market, enabling businesses to make informed decisions, optimize production processes, and capitalize on growth opportunities in this high-demand sector.
About Us:
Procurement Resource is an invaluable partner for businesses seeking comprehensive market research and strategic insights across a spectrum of industries. With a repository of over 500 chemicals, commodities, and utilities, updated regularly, they offer a cost-effective solution for diverse procurement needs. Their team of seasoned analysts conducts thorough research, delivering clients with up-to-date market reports, cost models, price analysis, and category insights.
By tracking prices and production costs across various goods and commodities, Procurement Resource ensures clients receive the latest and most reliable data. Collaborating with procurement teams across industries, they provide real-time facts and pioneering practices to streamline procurement processes and enable informed decision-making. Procurement Resource empowers clients to navigate complex supply chains, understand industry trends, and develop strategies for sustainable growth.
Contact Us:
Company Name: Procurement Resource
Contact Person: Amanda Williams
Email: sales@procurementresource.com
Toll-Free Number: USA Canada – Phone no: +1 307 363 1045 | UK – Phone no: +44 7537 132103 | Asia-Pacific (APAC) – Phone no: +91 1203185500
Address: 30 North Gould Street, Sheridan, WY 82801, USA