Introduction
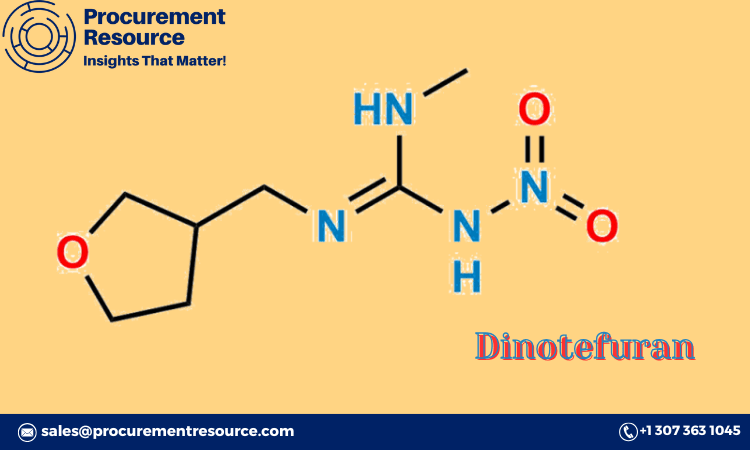
The Dinotefuran Production Process with Cost Analysis is crucial for understanding the steps involved in producing this powerful insecticide, along with the associated costs and resource requirements. Dinotefuran is a neonicotinoid insecticide used widely in agriculture and pest control. This report will cover the detailed production process, market drivers, raw material needs, and cost implications for businesses involved in Dinotefuran manufacturing.
Request Free Sample – https://www.procurementresource.com/production-cost-report-store/dinotefuran/request-sample
Procurement Resource Assessment: Dinotefuran Production Process
A comprehensive procurement resource assessment for Dinotefuran production involves sourcing essential raw materials and establishing reliable supplier partnerships. This process can significantly impact production efficiency, costs, and the quality of the final product. Key aspects include:
- Primary Ingredients: Specific chemical compounds are necessary for synthesizing Dinotefuran, requiring consistent sourcing to ensure production continuity.
- Supplier Evaluation: Finding reputable suppliers that meet quality standards and deliver on time is crucial. Many manufacturers work with multiple suppliers to mitigate risks related to availability and price fluctuations.
- Logistics and Supply Chain Optimization: Effective logistics planning helps minimize transportation costs, secure timely deliveries, and maintain an uninterrupted production flow.
- Sustainable Practices: As environmental concerns grow, more manufacturers are adopting sustainable practices, such as reducing waste and using greener raw materials whenever possible.
Dinotefuran Overview
Dinotefuran is a highly effective insecticide used to protect crops from a wide range of pests. It acts on the insect’s nervous system, disrupting their ability to function, and is particularly effective against sucking insects like aphids, whiteflies, and thrips.
Key Properties of Dinotefuran:
- Mode of Action: Targets insect nervous systems by binding to nicotinic acetylcholine receptors.
- Environmental Profile: Known for its effectiveness, Dinotefuran breaks down relatively quickly in the environment, reducing long-term contamination risks.
- Application Versatility: It can be applied as a spray, soil treatment, or through seed treatment, making it versatile for various agricultural needs.
Market Drivers
Several market drivers influence the production and demand for Dinotefuran:
- Agricultural Demand: With the growing need for effective pest management, especially in agriculture, Dinotefuran’s role as a reliable insecticide is critical.
- Pest Resistance Issues: As pests become resistant to traditional insecticides, there’s an increasing demand for alternative solutions like Dinotefuran, which remains effective against many resistant pest populations.
- Technological Advancements in Production: Advances in chemical synthesis and production efficiency are helping to reduce costs and improve the availability of Dinotefuran.
- Environmental and Regulatory Pressures: With environmental regulations tightening, Dinotefuran’s relatively rapid degradation in soil makes it more appealing in regions with strict environmental standards.
Raw Materials Requirements
The raw materials required for Dinotefuran production include:
- Primary Chemical Precursors: Compounds such as guanidine and other nicotinoid base chemicals are used in the synthesis process. These materials should be of high purity to ensure the efficacy of the final product.
- Catalysts and Solvents: Various catalysts aid the chemical reactions involved in Dinotefuran synthesis, while solvents are used to dissolve reactants and facilitate the reaction.
- Additives: Certain additives are sometimes introduced to stabilize the product and enhance its shelf life.
- Quality Control Reagents: Analytical reagents are needed to test the purity and quality of Dinotefuran at various production stages.
Costs and Key Process Information
The production costs and key steps involved in manufacturing Dinotefuran are as follows:
- Synthesis and Chemical Reactions: The synthesis process includes multiple steps, starting with the formation of the base compound and progressing through several stages of chemical modification. Each step requires specific conditions, such as temperature and pH control, to ensure successful reactions.
- Purification and Quality Control: Once synthesized, Dinotefuran is purified through techniques such as crystallization or distillation. These steps help remove any impurities, ensuring a high-quality final product suitable for agricultural use.
- Labor and Operational Costs: Highly trained personnel are necessary to oversee the production process, conduct quality tests, and ensure safety standards are met.
- Packaging and Compliance: As an insecticide, Dinotefuran requires special packaging to ensure safe storage and transport. Compliance with local and international regulations for pesticide production and distribution is also essential.
Looking for an Exhaustive and Personalized Report That Could Significantly Substantiate Your Business
For businesses interested in a deeper understanding of the Dinotefuran production process, a customized report can provide detailed insights specific to your operational and market needs. Such a report can include a complete cost analysis, raw material sourcing recommendations, and market trends to help you make informed decisions. Leveraging this information can lead to a competitive edge, especially in a field that requires strict adherence to regulatory standards and high-quality production outputs.
If you’re looking for an exhaustive and personalized report, connect with industry experts who can help tailor these insights to support your business strategy and optimize your production process.
About Us:
Procurement Resource is an invaluable partner for businesses seeking comprehensive market research and strategic insights across a spectrum of industries. With a repository of over 500 chemicals, commodities, and utilities, updated regularly, they offer a cost-effective solution for diverse procurement needs. Their team of seasoned analysts conducts thorough research, delivering clients with up-to-date market reports, cost models, price analysis, and category insights.
By tracking prices and production costs across various goods and commodities, Procurement Resource ensures clients receive the latest and most reliable data. Collaborating with procurement teams across industries, they provide real-time facts and pioneering practices to streamline procurement processes and enable informed decision-making. Procurement Resource empowers clients to navigate complex supply chains, understand industry trends, and develop strategies for sustainable growth.
Contact Us:
Company Name: Procurement Resource
Contact Person: Amanda Williams
Email: sales@procurementresource.com
Toll-Free Number: USA copyright – Phone no: +1 307 363 1045 | UK – Phone no: +44 7537171117 | Asia-Pacific (APAC) – Phone no: +91 1203185500
Address: 30 North Gould Street, Sheridan, WY 82801, USA