Isorhamnetin is a naturally occurring flavonoid, specifically a methylated derivative of quercetin, found in various plants and foods, such as sea buckthorn, Ginkgo biloba, and certain fruits and vegetables. Known for its antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, and anti-cancer properties, isorhamnetin has gained popularity in the fields of health and nutrition. This compound offers numerous benefits, making it highly desirable in the pharmaceutical, nutraceutical, and cosmetic industries. In this blog, we will explore the production process of isorhamnetin, its benefits, and its chemical structure.
What is Isorhamnetin?
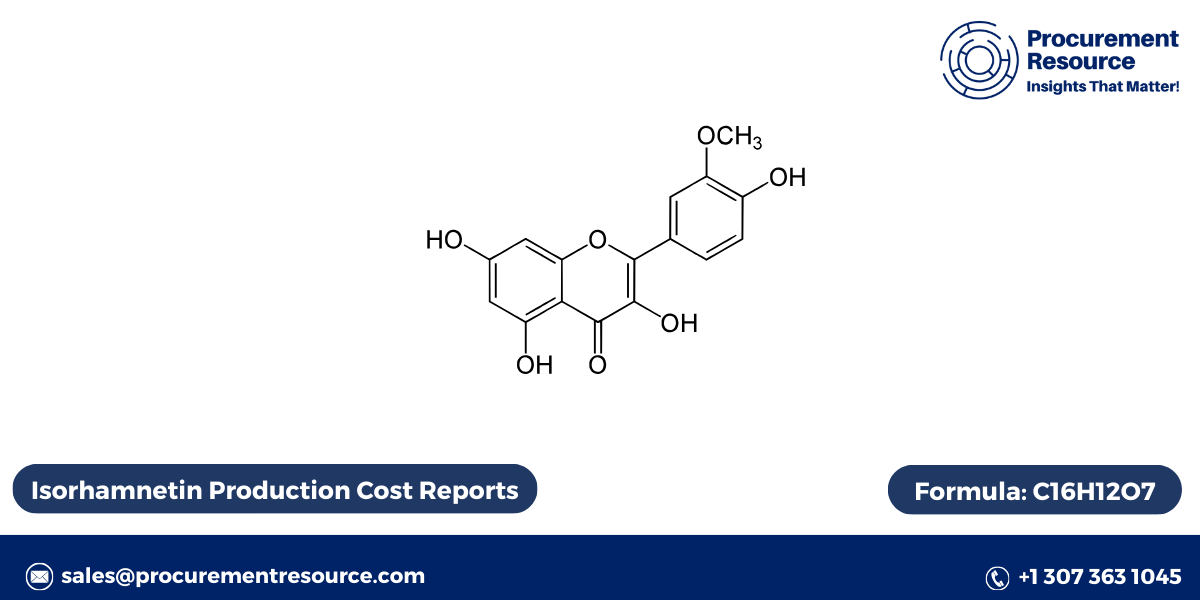
Isorhamnetin is a methylated form of quercetin, a well-known flavonoid. It belongs to the flavonol subclass of flavonoids and is characterized by its structure that includes hydroxyl and methoxy groups, which contribute to its biological activity. The chemical structure of isorhamnetin is:
- Molecular Formula: C₁₆H₁₂O₇
- Molecular Weight: 316.26 g/mol
- Structure: A benzopyran ring with hydroxyl groups at positions 3 and 5 and a methoxy group at position 3′
Request For Sample: https://www.procurementresource.com/production-cost-report-store/isorhamnetin/request-sample
The unique structure of isorhamnetin allows it to act as a powerful antioxidant and anti-inflammatory agent. These properties make it particularly useful in preventing and managing various health conditions.
Health Benefits of Isorhamnetin
Isorhamnetin offers several health benefits, largely due to its antioxidant and anti-inflammatory capabilities. Here are some of its most notable benefits:
- Antioxidant Properties: Isorhamnetin helps to neutralize free radicals, which are molecules that can damage cells and lead to chronic diseases such as cancer, heart disease, and diabetes. Its antioxidant power may help protect cells from oxidative stress, reducing the risk of these diseases.
- Anti-inflammatory Effects: Chronic inflammation is a known contributor to various diseases, including arthritis and cardiovascular disease. Isorhamnetin inhibits specific enzymes and pathways associated with inflammation, potentially reducing symptoms of inflammatory conditions.
- Cardiovascular Health: By helping reduce blood pressure, improve blood lipid levels, and prevent blood clot formation, isorhamnetin supports heart health. Studies have suggested that it may also improve endothelial function, which is vital for maintaining healthy blood vessels.
- Cancer Prevention: Preliminary research has shown that isorhamnetin may inhibit the growth of certain types of cancer cells, including breast and lung cancer cells. While more research is needed, its ability to inhibit cancer cell proliferation and induce apoptosis makes it a promising compound for cancer prevention and treatment.
- Neuroprotective Effects: Isorhamnetin may offer protection to the brain by reducing oxidative stress and inflammation. This could help in preventing neurodegenerative diseases such as Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s disease.
The Production Process of Isorhamnetin
The production of isorhamnetin involves extraction and isolation processes that are designed to ensure the purity and efficacy of the compound. This process can be carried out in several ways, including chemical synthesis, biotransformation, and extraction from natural sources. Here is an overview of the most common production methods:
- Extraction from Natural Sources:
- Step 1: Selection of Plant Source – Plants rich in isorhamnetin, such as sea buckthorn and Ginkgo biloba, are chosen as raw materials.
- Step 2: Preparation of Plant Material – The plant material is cleaned, dried, and ground into a fine powder to maximize the surface area for extraction.
- Step 3: Solvent Extraction – The powdered plant material is mixed with a suitable solvent, often ethanol or methanol, and allowed to steep for a specified duration to extract the flavonoids. This step may be followed by additional purification processes to enhance the concentration of isorhamnetin.
- Step 4: Filtration and Evaporation – The mixture is filtered to remove solid impurities, and the solvent is then evaporated under reduced pressure to obtain a crude extract.
- Step 5: Chromatographic Purification – Techniques such as column chromatography or high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) are used to purify the isorhamnetin from other compounds in the extract.
- Step 6: Drying and Packaging – The purified isorhamnetin is dried, often by freeze-drying, and then packaged for distribution.
- Biotransformation Process:
- This method involves the use of enzymes or microbial cultures to convert precursor compounds like quercetin into isorhamnetin. The process can be more cost-effective and environmentally friendly.
- Step 1: Fermentation – Microorganisms are cultivated in a fermentation medium containing quercetin.
- Step 2: Biotransformation – The microorganisms produce enzymes that convert quercetin to isorhamnetin through methylation.
- Step 3: Extraction and Purification – The isorhamnetin is extracted from the culture medium and purified using similar techniques as those used in natural extraction.
- Chemical Synthesis:
- Chemical synthesis of isorhamnetin is achieved through a series of organic reactions that introduce specific functional groups to form the final compound.
- Step 1: Methylation of Quercetin – Starting from quercetin, a methylation reaction is carried out using a methylating agent, such as methyl iodide, under controlled conditions.
- Step 2: Purification – The synthesized isorhamnetin is then purified using recrystallization or chromatography to ensure a high level of purity.
Challenges and Innovations in Isorhamnetin Production
The production of isorhamnetin, especially from natural sources, can face challenges related to the availability and quality of raw materials. Additionally, the extraction process may sometimes lead to low yields and require environmentally harmful solvents. To address these challenges, research is ongoing to develop more sustainable extraction techniques and improve the efficiency of biotransformation processes. Innovations in green chemistry and biotechnology are contributing to the development of cost-effective and eco-friendly production methods.
Isorhamnetin is a potent flavonoid with numerous health benefits, and its demand is growing in the health and wellness sectors. While its production involves complex extraction and purification processes, advancements in biotechnology are paving the way for more efficient and sustainable methods. With continued research, isorhamnetin has the potential to become a staple compound in the fight against chronic diseases, enhancing both physical and mental well-being.
By understanding the structure, benefits, and production process of isorhamnetin, industries and consumers can appreciate the importance of this valuable flavonoid. As we continue to explore natural compounds like isorhamnetin, we move closer to achieving a healthier and more sustainable future.
Contact Us:
Company Name: Procurement Resource
Contact Person: Endru Smith
Email: sales@procurementresource.com
Toll-Free Number: USA & Canada - Phone no: +1 307 363 1045 | UK - Phone no: +44 7537 132103 | Asia-Pacific (APAC) - Phone no: +91 1203185500
Address: 30 North Gould Street, Sheridan, WY 82801, USA