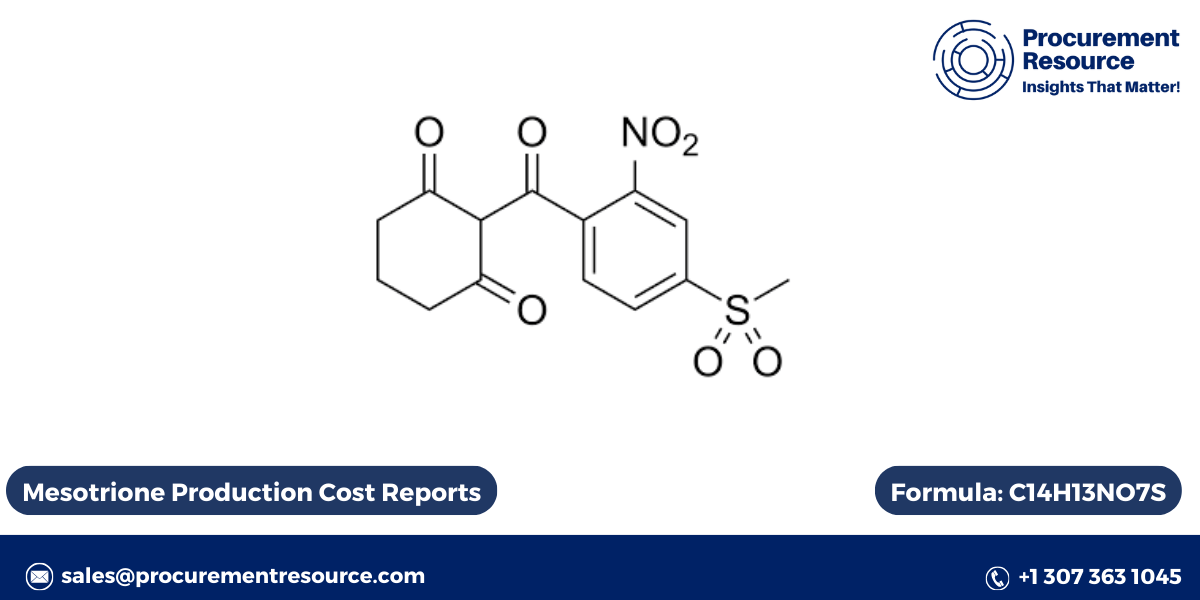
Mesotrione is a selective herbicide widely used in agriculture to control broadleaf weeds and grasses in crops such as corn. This herbicide belongs to the triketone family of herbicides and operates by inhibiting the enzyme 4-hydroxyphenylpyruvate dioxygenase (HPPD), which is crucial for the synthesis of carotenoids in plants. The absence of carotenoids leads to the destruction of chlorophyll, causing bleaching and eventual death of the weeds. This article explores the production process of Mesotrione, its cost factors, herbicide uses, labeling information, and its toxicity levels.
Mesotrione Production Process
The production of Mesotrione involves several steps in chemical synthesis, often starting with raw materials such as benzoyl acetone or derivatives of nitrobenzenes. The following are key stages in its manufacturing process:
Request For Sample: https://www.procurementresource.com/production-cost-report-store/mesotrione/request-sample
- Raw Material Procurement: The primary raw materials include derivatives of benzoyl acetone and other chemical reagents necessary for the synthesis of triketones.
- Reaction Process: The reaction begins with the condensation of benzoyl acetone to form the triketone core structure. This is achieved through controlled chemical reactions involving the use of appropriate catalysts and reagents.
- Purification and Crystallization: After the synthesis, the crude product undergoes purification to eliminate impurities. This involves crystallization and filtration techniques to obtain a pure compound.
- Final Product Formulation: The purified Mesotrione is formulated into its final product form, often as a liquid concentrate or a water-dispersible granule.
- Quality Control: Throughout the production process, quality control measures are applied to ensure the final product meets safety, efficacy, and environmental standards. The product is tested for purity, potency, and residual solvents to confirm compliance with regulatory standards.
Mesotrione Production Cost
The production cost of Mesotrione varies based on several factors:
- Raw Material Costs: The price of raw materials, particularly chemical reagents and catalysts, can significantly impact the overall production cost.
- Energy Consumption: Manufacturing Mesotrione is energy-intensive, and fluctuations in energy prices (electricity, fuel, etc.) can influence production costs.
- Labor and Operational Costs: Skilled labor, maintenance of equipment, and other operational expenses contribute to the cost structure.
- Regulatory Compliance: Adherence to environmental regulations and safety standards often adds to the overall production cost, as manufacturers need to implement stringent quality control systems and waste management protocols.
- Scale of Production: Larger-scale production benefits from economies of scale, reducing the cost per unit, while smaller operations might face higher costs due to inefficiencies in production.
Mesotrione Herbicide Uses
Mesotrione is primarily used in the agricultural sector to manage a wide variety of broadleaf weeds and grasses. Some of its key applications include:
- Corn Crops: Mesotrione is most commonly applied in corn production to control weeds that can significantly reduce crop yields. It can be applied pre-emergence or post-emergence, giving farmers flexibility in weed management.
- Sorghum: It is also effective in controlling weeds in sorghum fields.
- Other Crops: Although its primary use is in corn, some formulations of Mesotrione are registered for use in other crops, such as sugarcane and turfgrass.
Mesotrione Herbicide Label
When using Mesotrione herbicide, it is important to adhere to the label instructions to ensure effective application and safety. Key information found on the herbicide label includes:
- Application Rates: The label specifies the recommended rates of application, which vary depending on the target crop and weed species.
- Timing of Application: Instructions on whether the herbicide should be applied pre-emergence or post-emergence are included, with guidance on the timing relative to the growth stages of crops and weeds.
- Safety Precautions: The label provides safety measures for handling, including the use of personal protective equipment (PPE) like gloves and masks to minimize exposure to chemicals.
- Environmental Restrictions: It also outlines guidelines to prevent contamination of water sources and sensitive ecosystems, ensuring the herbicide is applied in a manner that minimizes its environmental impact.
Mesotrione Herbicide
Mesotrione is a highly effective herbicide due to its selective mode of action, targeting weeds while minimizing damage to crops. It is applied either in pre-emergence (before weeds appear) or post-emergence (after weeds have sprouted). The herbicide works by inhibiting HPPD, disrupting the production of protective carotenoids in weeds. This leads to a buildup of toxic compounds, bleaching the plants and ultimately killing them.
Key features of Mesotrione herbicide include:
- Broad-Spectrum Control: It controls a wide range of broadleaf weeds, including giant ragweed, common lambsquarters, and velvetleaf.
- Crop Safety: When used correctly, Mesotrione is safe for many crops, particularly corn, without causing crop damage.
- Flexible Application: The herbicide can be used in both pre- and post-emergence stages, offering flexibility to farmers.
Mesotrione Toxicity
While Mesotrione is an effective herbicide, its toxicity is a concern for both human health and the environment.
- Human Toxicity: Mesotrione is classified as having low toxicity for humans when used as directed. However, exposure through inhalation or skin contact can cause mild irritation. As a precaution, users should always wear protective clothing and follow the safety instructions provided on the herbicide label.
- Environmental Toxicity: Mesotrione poses a risk to aquatic ecosystems if not applied correctly. It can contaminate water sources through runoff, potentially harming aquatic plants and animals. To mitigate this, it is important to follow the label’s guidelines regarding buffer zones and water protection measures.
- Breakdown and Persistence: In soil, Mesotrione is broken down by microbial activity and has a moderate persistence, depending on the environmental conditions such as temperature, soil type, and moisture. This degradation reduces its long-term impact on the environment but requires careful consideration during application to avoid leaching into groundwater.
Mesotrione is a valuable tool in modern agriculture, offering effective control of broadleaf weeds while maintaining crop safety. Its production involves sophisticated chemical processes, and its use must adhere to strict guidelines to ensure both efficacy and environmental safety. By understanding the production costs, herbicide uses, label instructions, and toxicity, farmers and agricultural professionals can make informed decisions about its application to maximize crop yields and minimize environmental impact.
Contact Us:
Company Name: Procurement Resource
Contact Person: Endru Smith
Email: sales@procurementresource.com
Toll-Free Number: USA & Canada - Phone no: +1 307 363 1045 | UK - Phone no: +44 7537 132103 | Asia-Pacific (APAC) - Phone no: +91 1203185500
Address: 30 North Gould Street, Sheridan, WY 82801, USA